Effect of the Oil Industry on Batteries
Investments in the battery industry and related technologies have grown so fast in the last decade. Many battery plants have been installed all around the world. The world’s top car manufacturers are spending massively to acquire a more significant share of the EVs market. Some car manufacturers such as Tesla, General Motors, and Volkswagen plan to have their battery giga-factories and even raw materials supply chain. China dominates raw materials required for batteries, and the United States is planning to have a domestic supply chain of nickel, cobalt, manganese, and graphite. Battery companies are developing new battery chemistries with less dependent critical substances such as nickel and graphite. Battscout has published articles on lithium iron phosphate cathode patent registration and patent landscape reports on silicon as a new solution for battery anode.
Lithium-ion batteries were invented in the 1970s and were commercialized by Sony in the 1990s. However, the battery experienced no significant growth until 20 years later. Some reasons include environmental concerns and governments policies to restrict the production of vehicles based on fossil fuels. But these reasons could occur decades ago. A question glances here: Why is the battery industry turned out to be a hot topic?
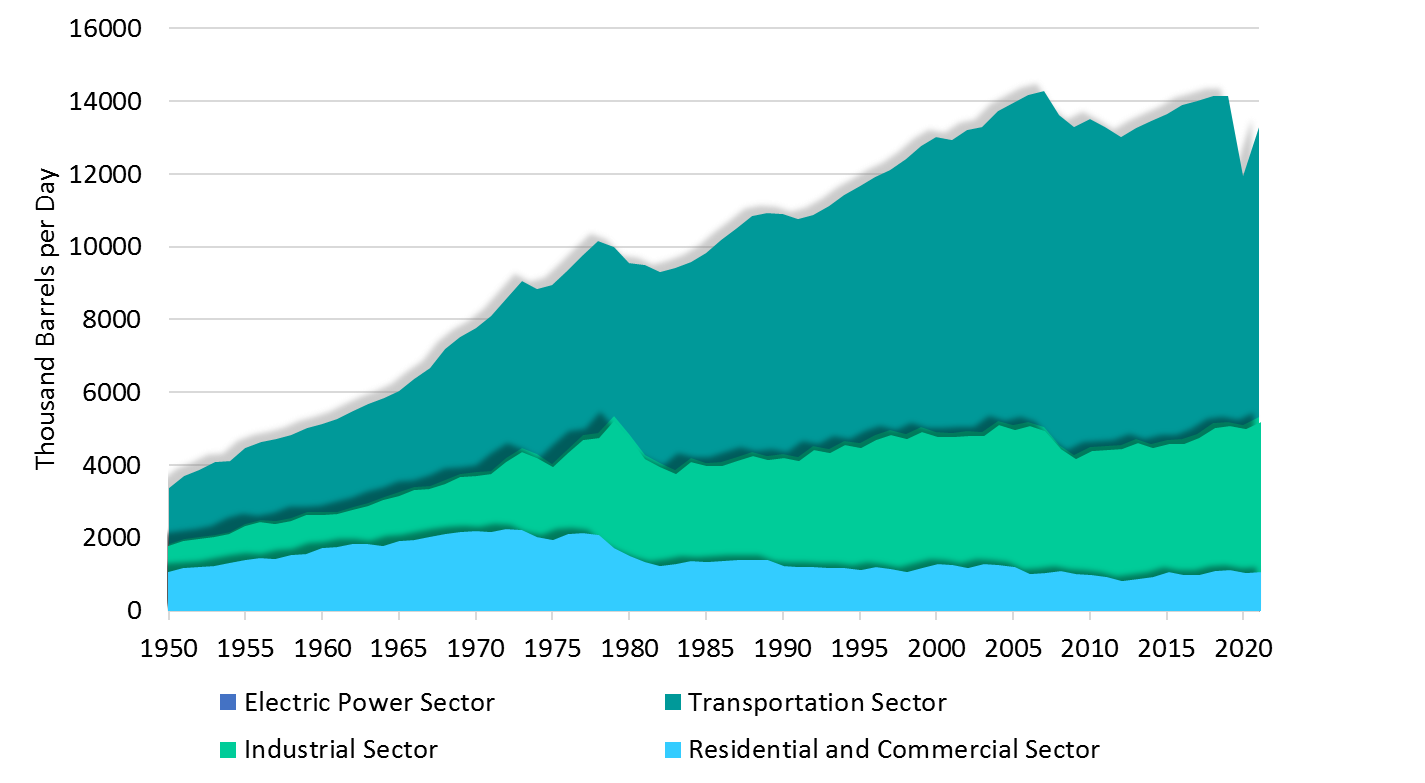
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) data, in 2021, 67% of petroleum products in the U.S. are consumed for transportation, while industrial, residential, and electric power sectors have a share of 27%, 5.5%, and 0.5%. This fact means that transport in the world relies on oil.
|
|
|
U.S. Consumption of Petroleum Products by Sector (1950-2021). (Source: eia.gov) |
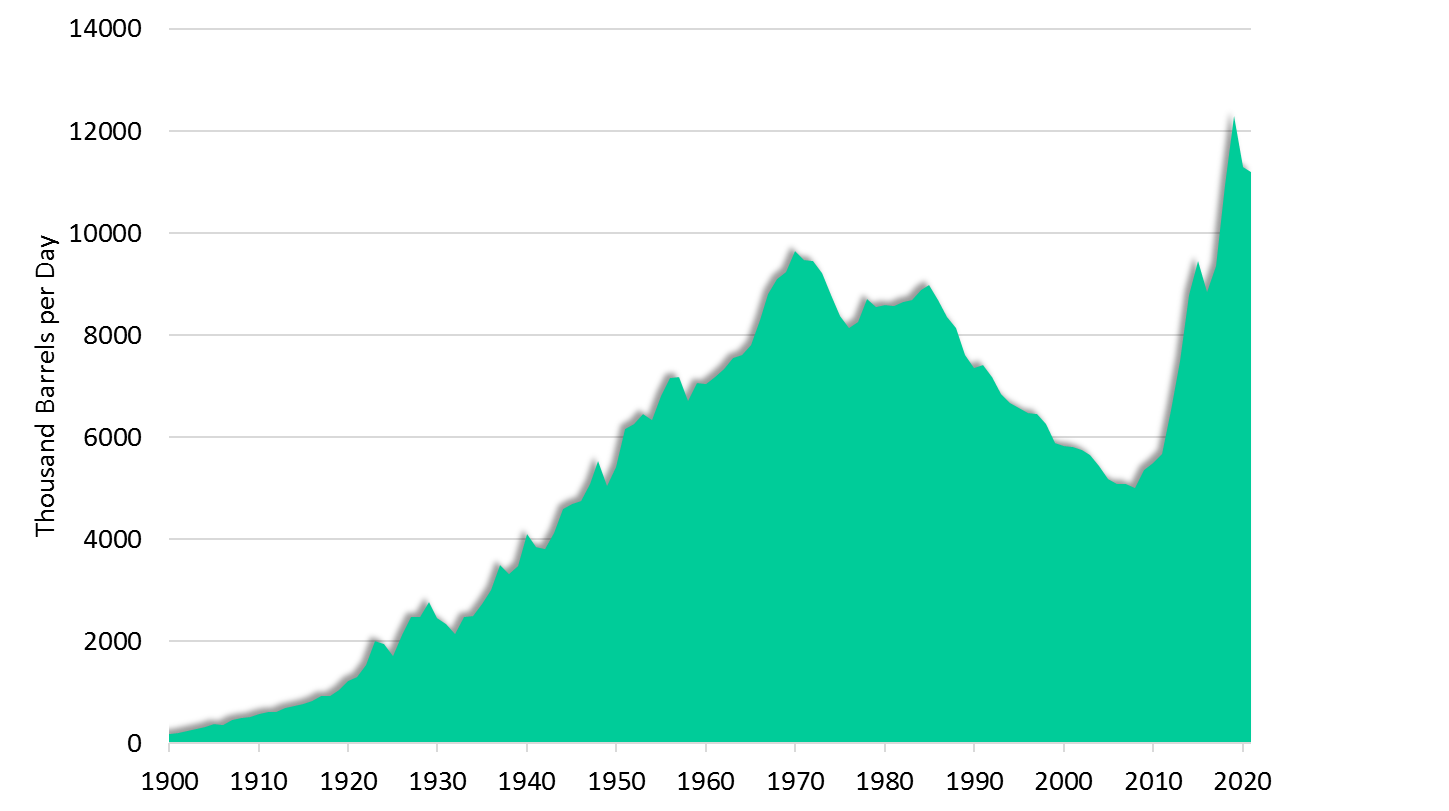
Most oil fields in the U.S. were discovered in the 1930s. The U.S. achieved its peak oil production forty years later, in the 1970s. The production of shale oil creates another peak after 2008. The EIA predicted a rise in 2021 which seems to be happening. The problem with shale oil is that each field is depleted after only 12 months to 25% of its initial capacity. Drilling horizontally and hydraulic fracturing are the leading technologies in shale oil production. These advanced technologies make shale oil an expensive type of oil. In addition, more wells must be drilled to produce it.
|
|
|
U.S. Oil Production. (Source: eia.gov) |
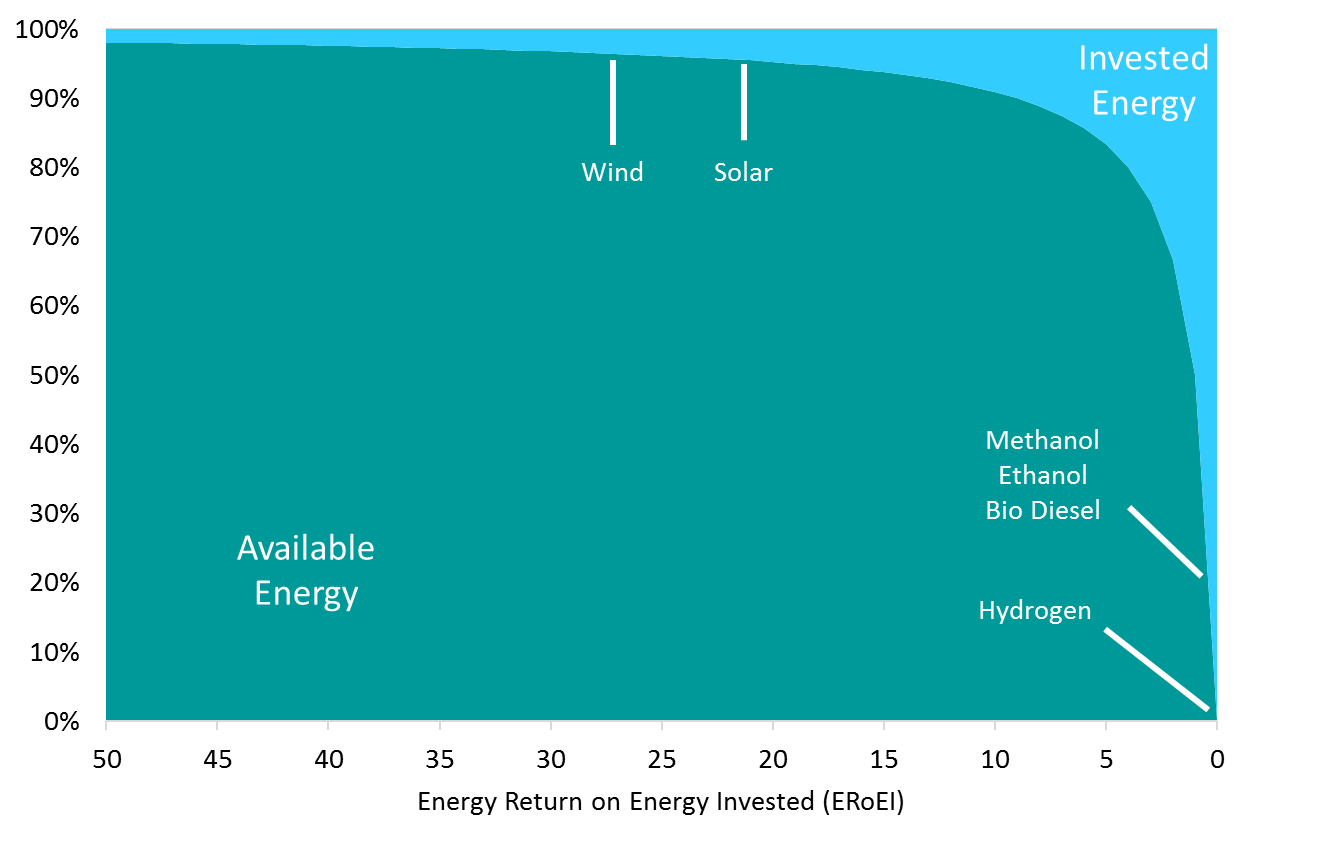
Energy return on energy invested (ERoEI) measures the ratio between the usable energy returned during the lifetime of a system to the energy investment needed to make it usable. Sustainable energy sources such as methanol, biodiesel, and ethanol have an ERoEI of less than 3:1. It is noticeable that hydrogen has a zero ERoEI because it is a carrier of energy, not a source; in other words, energy should be consumed to obtain hydrogen. These liquid candidates are not comparable to petroleum to fulfill the demand of the transportation industry. The only sources with an efficient ERoEI ratio are wind and solar energy. These two sources produce electricity and not liquid. Vehicles, ships, and aircraft are designed to use fluid sources. The only option for storing electricity in cars is the battery. Without batteries, no transportation will be available in the following decades. So it pushes the industry to develop batteries with more storage capacity, safety, durability, and a reasonable price.
|
|
|
The Energy Cliff. |